Building a home is a major milestone in life. Whether it’s a compact family house or a sprawling villa, proper planning, budgeting, and decision-making are critical. This guide dives deep into the essentials of building a home, focusing on cost-saving measures, sustainability, and making your home a perfect fit for your needs.
Key Considerations Before Building a Home
1. Land and Location Selection
- Choosing the Right Location:
- Opt for a location with convenient access to transportation, schools, markets, and healthcare facilities.
- Ensure the area has good natural ventilation and sunlight.
- Soil Quality and Testing:
- Conduct soil testing to determine its bearing capacity. Weak or clayey soil may require additional reinforcement for the foundation.
- Legal Documentation:
- Verify the land ownership documents and ensure the zoning regulations allow residential construction.
- Obtain all necessary permits and approvals from local authorities.
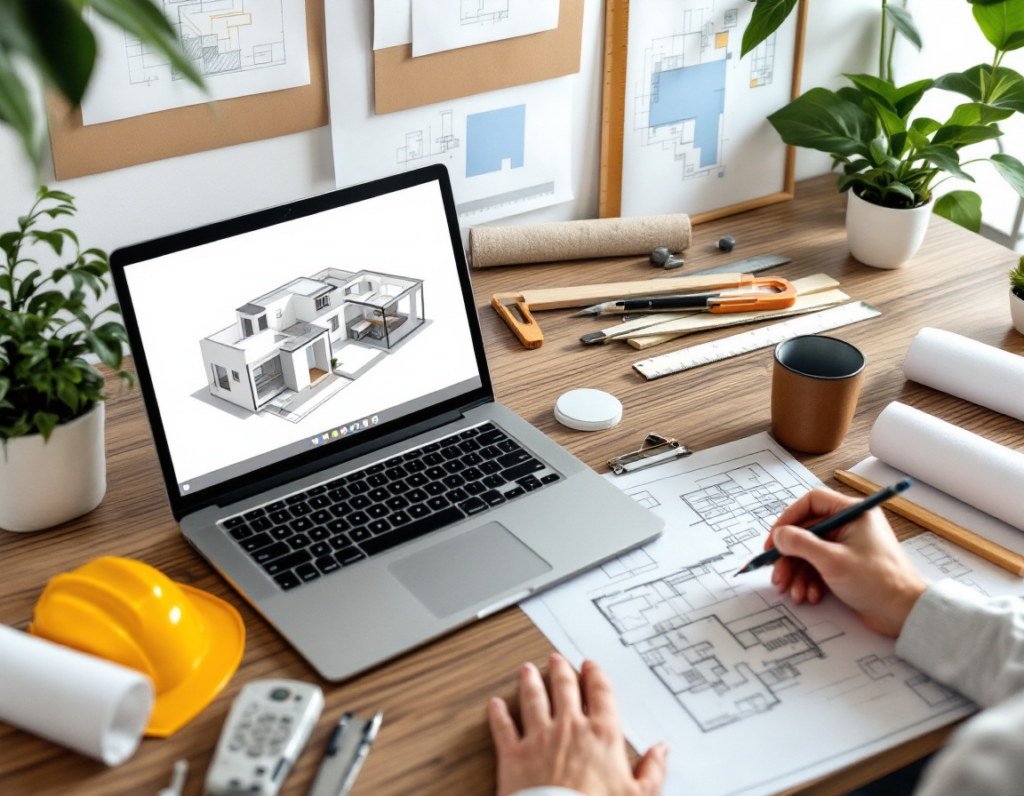
2. Designing and Planning
- Space Allocation:
- Plan the number of rooms and their sizes based on family needs. A family of 4-5 may require three bedrooms, a living room, a dining area, and two bathrooms.
- Maximize space utilization by adopting open layouts for common areas like the kitchen and dining.
- Sustainable Design:
- Position the house to allow for natural light and cross ventilation, reducing the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning.
- Plan for future expansions without compromising the current design.

3. Budget Planning
- Major Cost Components:
- Foundation and Land Development: 15-20%
- Construction Materials: 30-40%
- Labor Costs: 15-20%
- Finishing and Interior Design: 10-15%
- Cost-Saving Tips:
- Use local materials that are durable and budget-friendly.
- Consider prefabricated or modular construction for faster and cost-efficient building.
4. Choosing Durable Materials
- Primary Materials:
- Cement: Opt for high-grade cement (OPC 43 or 53) for durable construction.
- Steel: Use TMT steel bars for strong and earthquake-resistant structures.
- Bricks: Use fired bricks or concrete blocks for long-lasting walls.
- Eco-Friendly Materials:
- Consider recycled materials, bamboo, or compressed earth blocks for sustainability.
- Waterproofing Solutions:
- Apply waterproof coatings on the foundation and roof to prevent moisture damage.
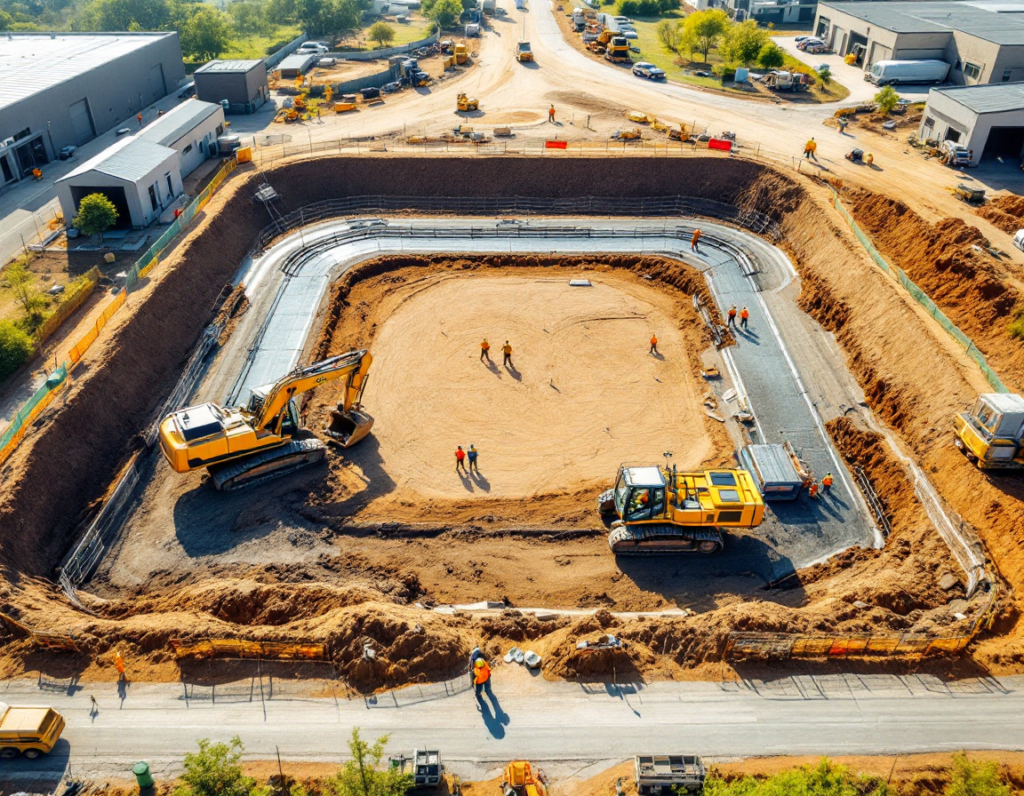
5. Construction Process
- Foundation:
- Choose the type of foundation (shallow or deep) based on soil conditions.
- Treat the foundation with anti-termite solutions for added protection.
- Structure and Frame:
- Reinforced concrete frames or steel frames are ideal for durability and flexibility.
- Prefabricated frames save time and cost for small houses.
6. Electrical, Plumbing, and HVAC Installations
- Electrical System:
- Install energy-efficient LED lighting, smart switches, and surge protectors.
- Ensure proper grounding for safety.
- Plumbing System:
- Use high-quality PVC or copper pipes to prevent leaks.
- Install water-saving fixtures to reduce water consumption.
- HVAC System:
- Choose energy-efficient air conditioning and heating systems.
- Install ventilation systems with air purifiers to maintain air quality.
7. Sustainability Measures
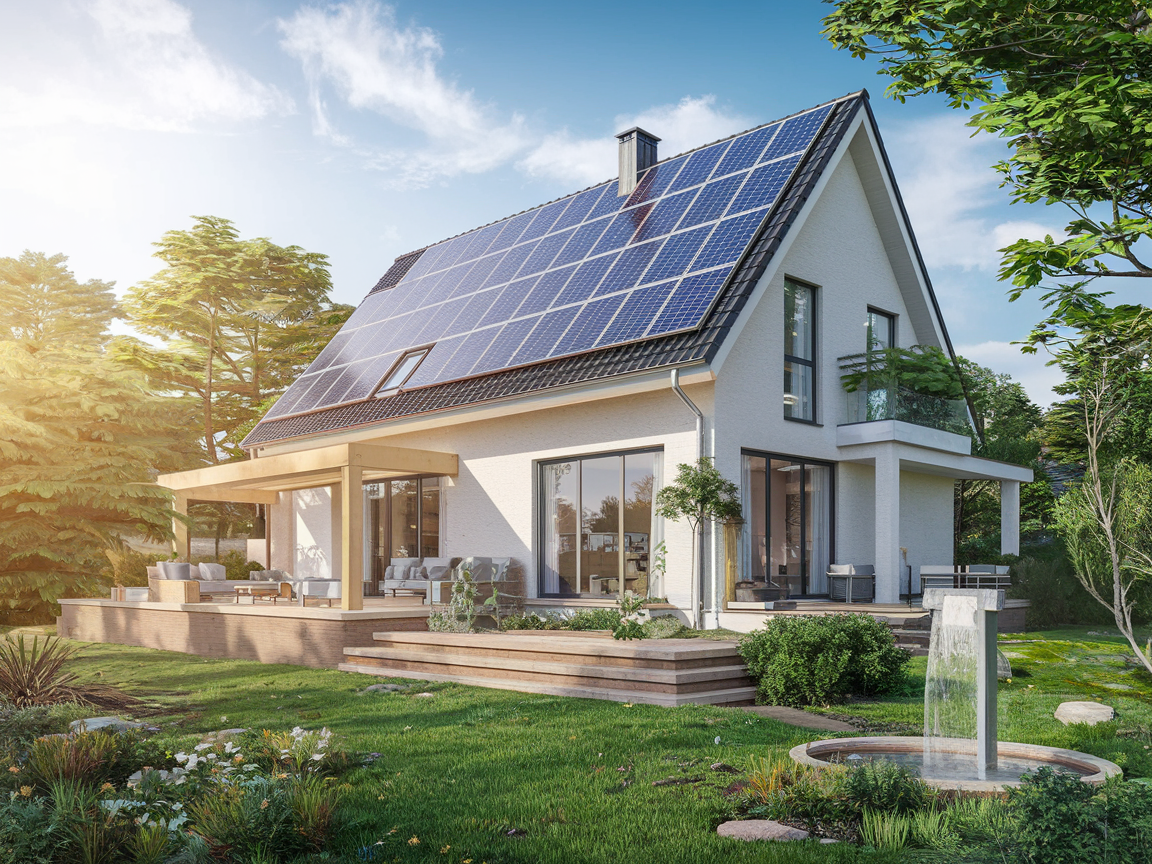
- Solar Panels:
- Install solar panels on the roof to reduce electricity bills and dependence on the grid.
- Rainwater Harvesting:
- Set up a system to collect and store rainwater for irrigation or household use.
- Insulation:
- Use thermal insulation in walls and roofs to regulate indoor temperatures naturally.

8. Finishing and Maintenance
- Finishing Touches:
- Choose weather-resistant paints and finishes.
- Use high-quality floor tiles or wood for durability and aesthetics.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Schedule regular checks for plumbing leaks, electrical faults, and HVAC cleaning to prolong the life of your home.

Conclusion
Building a home is not just about bricks and mortar—it’s about creating a space that’s safe, comfortable, and sustainable. Proper planning, budget allocation, and professional advice can help you construct a home that suits your family’s needs while being environmentally conscious and cost-effective. Invest in quality, think long-term, and build a house that becomes a home for generations.



Building a home is indeed a significant step that requires careful thought and preparation. It’s inspiring to see the emphasis on sustainability and long-term planning in this guide. Creating a space that’s both functional and eco-friendly is essential in today’s world. How can one balance cost-saving measures with the need for high-quality materials and sustainable practices?
Агрегатор.топ – единый агрегатор для контрактов, финансов и страхования.
Агрегатор контрактов – подряды, товары и услуги в одном месте.
Агрегатор финансов – банковские гарантии, лизинг, страхование от 80+ банков и 20+ лизинговых и страховых компаний.
Одна заявка – множество предложений. Экономьте время и деньги.